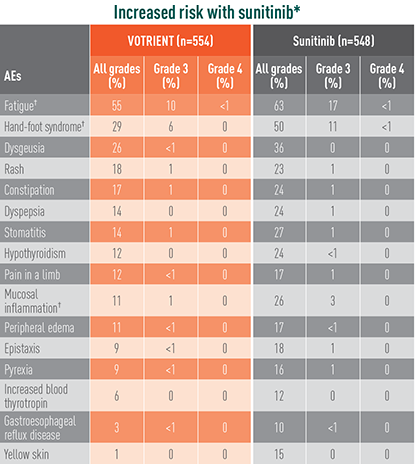
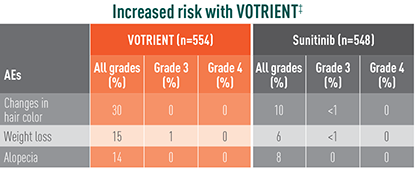
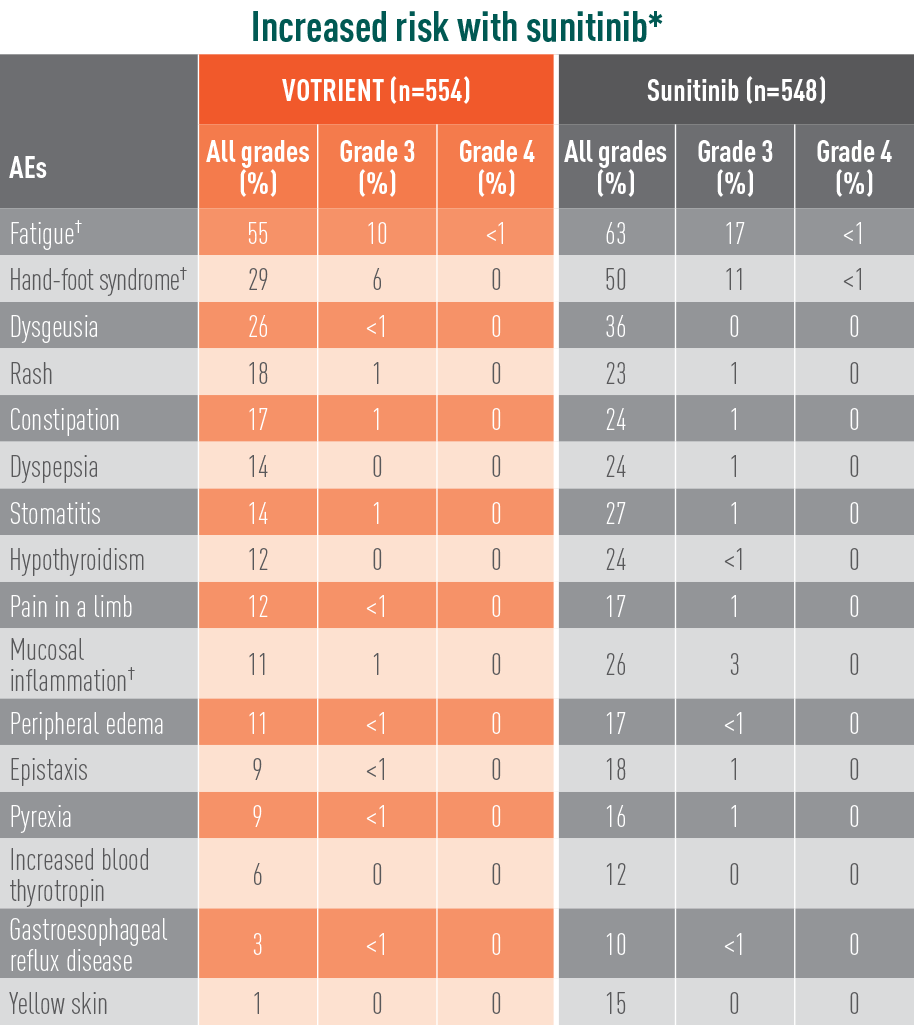
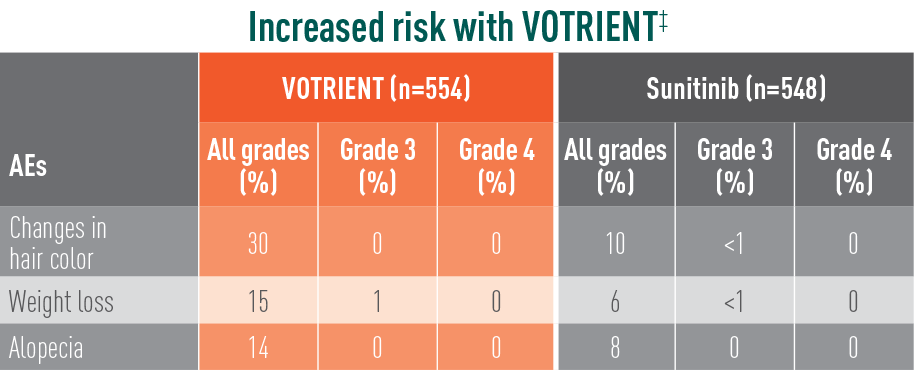
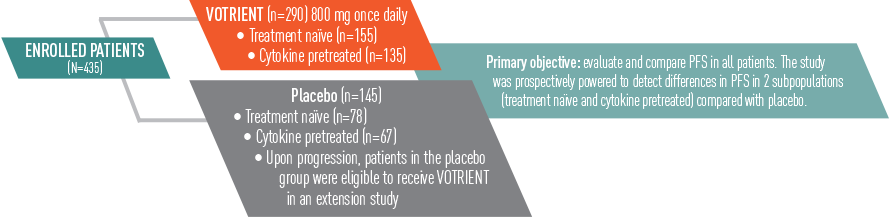
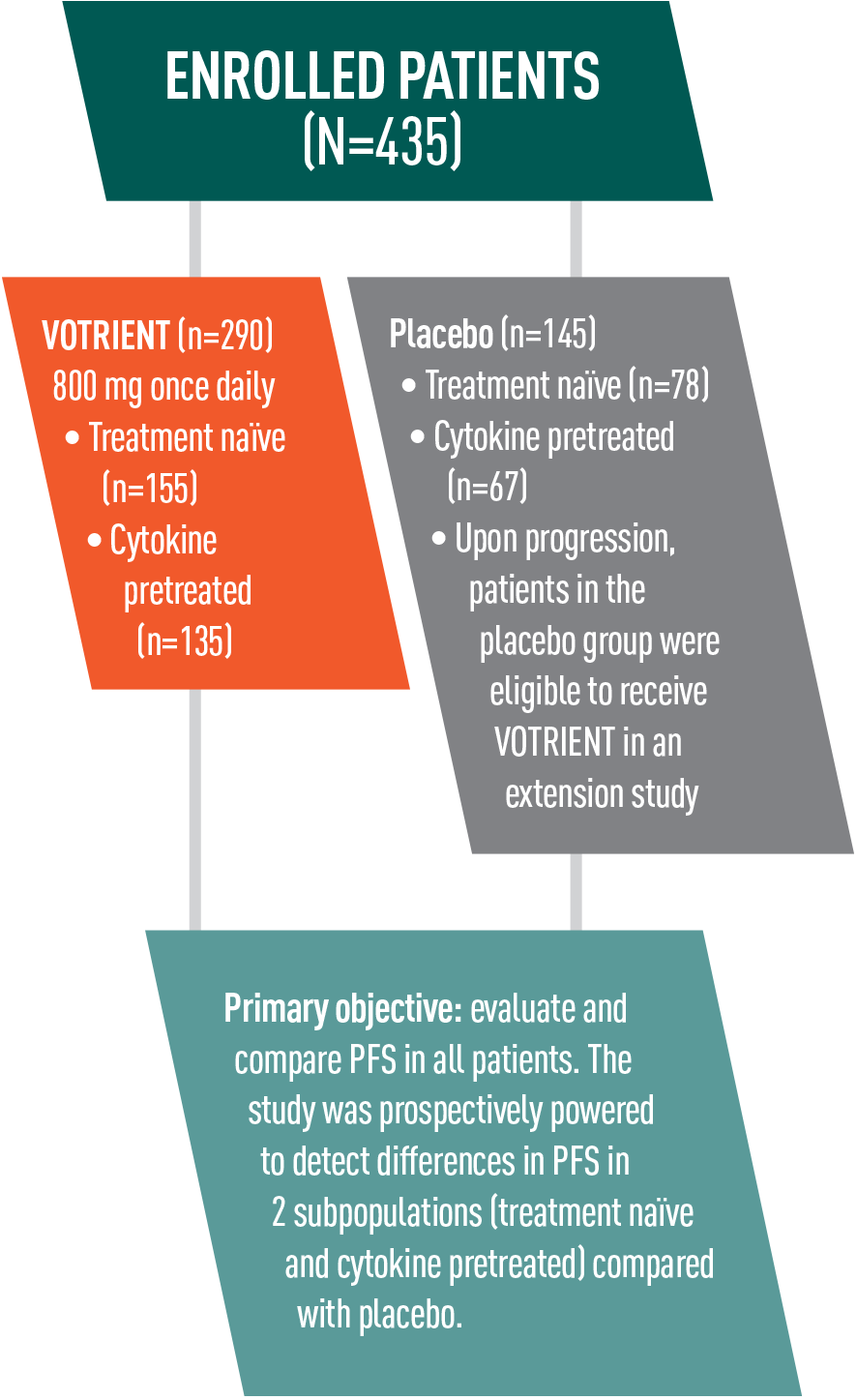
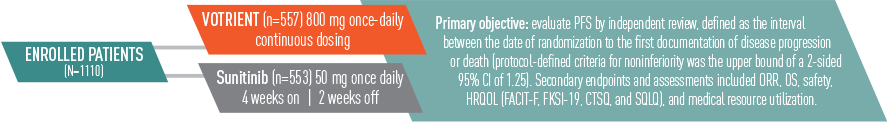
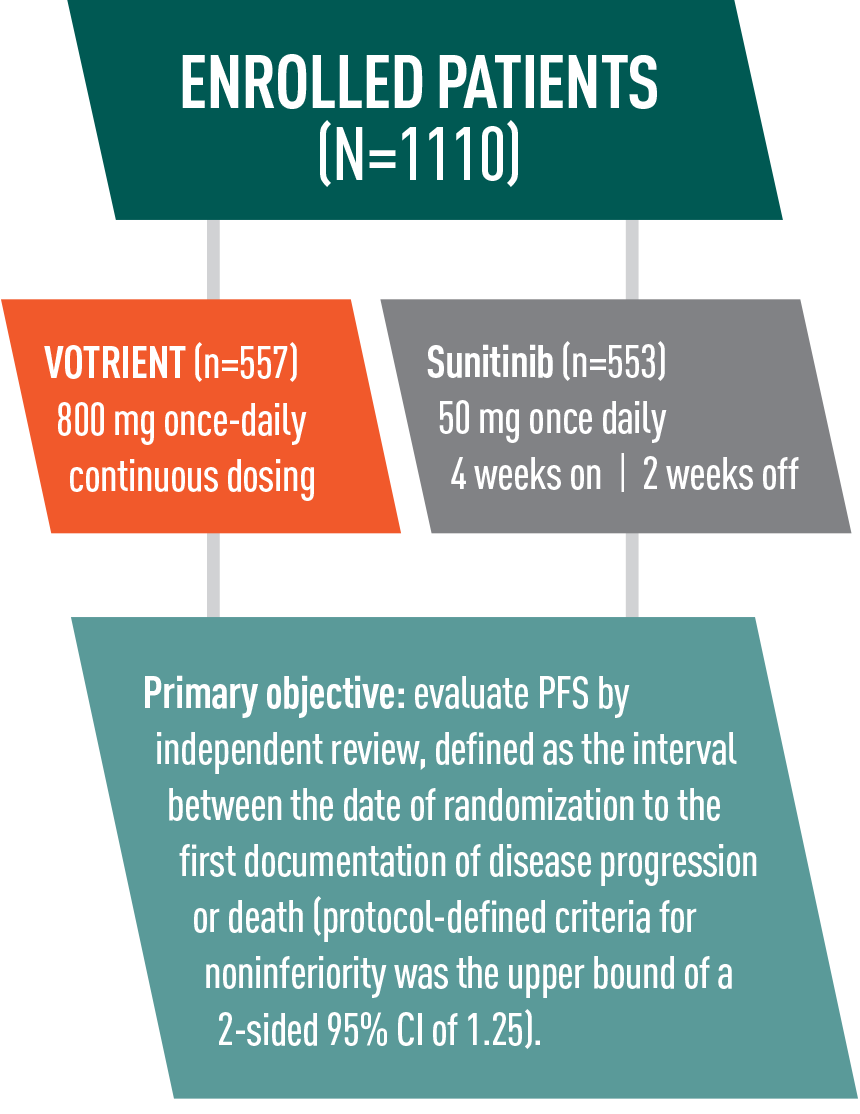
VOTRIENT—Differentiated safety profile from sunitinib in COMPARZ1
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) differed with sunitinib
Treatment-emergent AEs in >10% of patients in COMPARZ
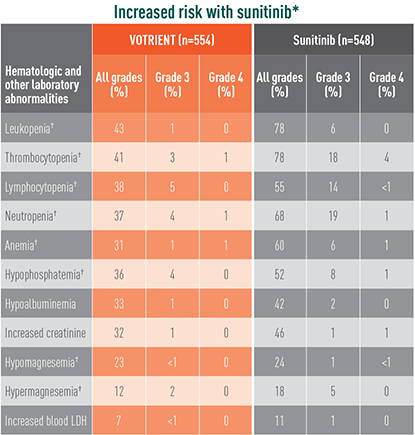
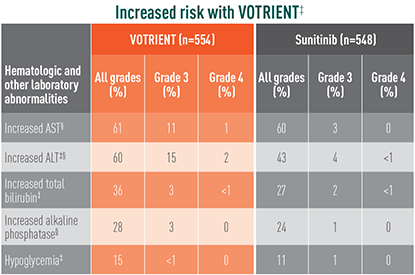
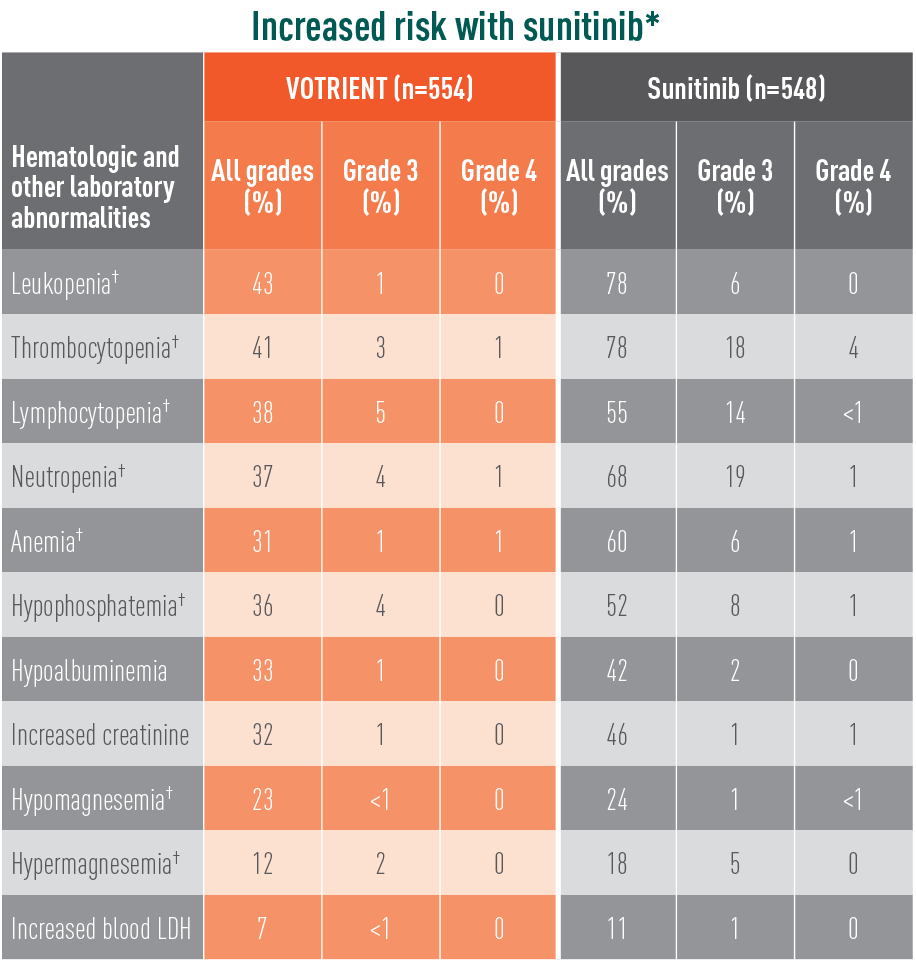
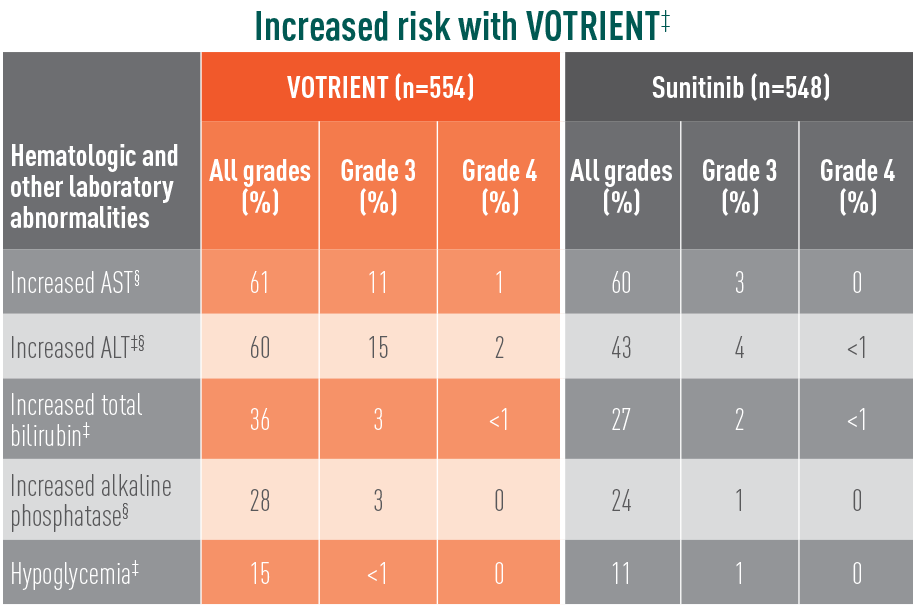
Grade 3/4 laboratory abnormalities differed with sunitinib
Laboratory abnormalities showing significant difference in relative risk in COMPARZ
The difference in relative risk was considered significant when the 95% CI did not include unity. These CIs were not corrected for multiple comparisons.
*The relative risk of an event of any grade was significantly higher with sunitinib than with VOTRIENT (except for hypomagnesemia).
†The relative risk of a grade 3/4 event was significantly higher with sunitinib than with VOTRIENT.
‡The relative risk of an event of any grade was significantly higher with VOTRIENT than with sunitinib.
§The relative risk of a grade 3/4 event was significantly higher with VOTRIENT than with sunitinib.
References: 1. Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):722-731. 2. VOTRIENT [summary of product characteristics]. Camberley, UK: Novartis Europharm Limited; February 2018.